To ensure quantitive measurement of the code quality, specific Standards and Technical Reports have been defined: for DPM code the verification methodology is defined in the ISO/IEC TR 29158 (that includes the AIM DPM-1-2006 Quality Guideline).
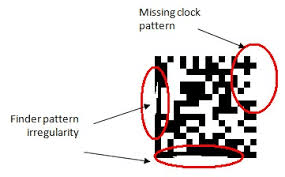
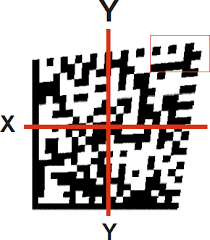
The scope to the ISO/IEC TR 29158 Standard is to define methodologies for the measurement of specific attributes of two-dimensional code symbols, defining methods for evaluating and grading these measurements and finally classify the code into five quality classes or grades: A, B, C, D and F.
The higher the class the higher the reliability of the reading process, F grade symbols are unlikely to be read successfully in most environments.
The OVERALL quality of the code is defined by the lowest resulting grade within the evaluated set of individual parameters.
To perform a reliable analysis of a code, specific measuring instruments, calles Certified Verifiers, are available on the market. These instruments embed standardized lighting systems, lenses and certified algorithms to objectively evaluate the quality of the code, providing a Quality Report with quantitative information about the code properties.
Verifiers are widely used to evaluate and certify the quality of the so called "golden sample" or "approved quality sample" to be used as the reference in mass production to ensure fail proof readings.
As other standard measurement instruments, Certified Verifiers are dedicated to operate in controlled environments, and typically are not suitable to monitor code quality in real wold production environments.
Code acquisition in a real production environment is sensitive to ambient light variation, mechanical vibration, electrical noise, degredation of the LED light system, etc. These fluctuations are not compatible with absolute and standardized measurement of the grade and cause, for example, the grade of the same samples measured several times to actually give different values.
In automatic production processes it is important to constantly monitor in-line the quality of the marking in order to scrap non - readable or poorly readable components.
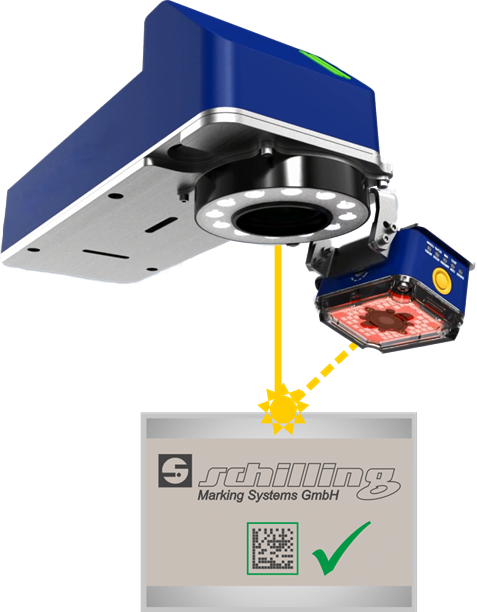
For the in-line quality check of the just-applied codes, industrial readers, like VISION are widely used, to perform comparative analysis of the code quality, monitoring variation in a real harsh production environment.
Even though VISION uses a grading library fully compliant with ISO/IEC standards, it does not take into consideration the external environmental lighting parameters such as aperture, wavelength and illumination angle which can in any case affect the scan grade. For this reason VISION can be used to monitor veriations in code quality but cannot be considered as Certified Verifier.
VISION is the treceability solution that ensures code quality in real production environments and combines into one single graphical user interface the flexibility of laser marking and the reliability of industrial code imagers.
VISION allows collecting multiple measurements and computes the statistical dispersion of each individual quality parameter, measuring and considering the contribution of each individual parameter.
This statistical approach allows real sample quality threshold training and a simple and immediate visualization of the quality spread for each code parameter.
This fully automatic quality training process provides a so called quality profile (patent pending) that always includes all the relevant quality parameters.